Geologists from Durham College and elsewhere have found a panorama that seems to have been formed by rivers at the least 14 million years in the past and even perhaps earlier than the preliminary progress of East Antarctic ice about 34 million years in the past.

jamison et al. Uncover large-scale pre-glacial landscapes preserved beneath the East Antarctic ice sheet regardless of hundreds of thousands of years of ice cowl. Picture credit score: Jamison et alMon: 10.1038/s41467-023-42152-2.
The Earth’s local weather is altering quickly and is on observe to achieve temperatures just like these discovered 34 to 14 million years in the past (between 3 and seven levels Celsius larger than in the present day).
Understanding how the Antarctic ice sheet has modified up to now helps inform the way it will evolve sooner or later attributable to ongoing local weather change.
That is vital as a result of the ice sheet presently incorporates the equal of about 60 meters of potential sea degree rise.
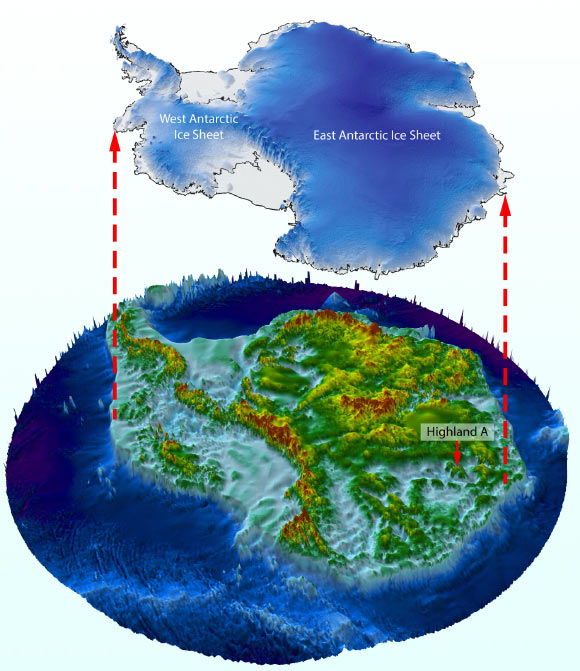
Ice-penetrating radar might be used to see the panorama below the ice and decide how the ice sheet modified earlier than the age of satellites.
Professor Stuart Jamieson, from Durham College, mentioned: “The land beneath the East Antarctic ice sheet is much less identified than the floor of Mars.”
“And that is an issue as a result of this panorama controls the way in which ice flows in Antarctica, and it controls the way in which it would reply to previous, current and future local weather change.”
“So, we’re finding out a small portion of this panorama in additional element to see what it may possibly inform us in regards to the evolution of the panorama and the evolution of the ice sheet.”
“And what we discovered is an historical land floor that was not eroded by the ice sheet, and as a substitute seems to have been created by rivers earlier than the looks of ice.”
“This tells us that there has not been lots of change on this specific space, which means that though this a part of the ice sheet could have retreated throughout hotter instances up to now, circumstances at this location most likely haven’t modified a lot,” he mentioned. This helps us perceive how the ice sheet will reply to future and ongoing warming.
Professor Jamieson and his colleagues used satellites and radar to investigate the panorama beneath the East Antarctic ice sheet within the Aurora-Schmidt basins inside the Denman and Totten glaciers.
They discovered that the panorama consists of three elevated river-carved blocks, separated by deep troughs, and situated solely about 350 kilometers from the sting of the ice sheet.
These blocks fashioned earlier than the Ice Age, when rivers crossed the area to the shoreline that opened up throughout the breakup of Gondwana.
The breakup of this supercontinent additionally brought on valleys to type between highland plenty, earlier than the highlands turned glacial.
The researchers level out that the ice over the area has remained largely steady over hundreds of thousands of years regardless of heat durations.
“It’s exceptional that this panorama, ‘hidden in plain sight’ for therefore a few years, can inform us rather a lot in regards to the early and long-term historical past of the East Antarctic ice sheet, in addition to serving to us perceive how this might have occurred.” “They’re evolving in response to future local weather change,” mentioned Professor Neil Ross of Newcastle College.
“This has been a slow-burn mission, however now it has come to fruition in an thrilling paper involving a implausible analysis group.”
Professor Jamieson mentioned: “We’ll proceed to discover the panorama, doing our greatest to fill within the gaps the place surveys are missing, and use that info to grasp how the ice sheet and the underlying panorama have modified over its lengthy historical past.”
the Stady It was revealed within the journal Nature Communications.
_____
SSR Jamison et al. A panorama of an historical river preserved beneath the East Antarctic ice sheet. Nat Frequent 14, 6507; Two: 10.1038/s41467-023-42152-2